miRCURY LNA miRNA Inhibitors are antisense oligonucleotides with perfect sequence complementary to their targets. When introduced into cells, they sequester the target miRNA in highly stable heteroduplexes, effectively preventing the miRNA from hybridizing with its normal cellular interaction partners.
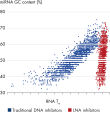
The potency of miRNA antisense inhibitors is determined by their affinity for their miRNA target and their biological stability. The affinity of normal inhibitors with conventional nucleotide chemistry is a function of the GC content of the miRNA target. Since the GC content of miRNAs can vary from 5–95%, potencies of such inhibitors will vary greatly according to the miRNA sequence, with essentially no potency with AT-rich miRNAs.
Design
We have exploited the high affinity properties of
LNA chemistry to create T
m-normalized miRCURY LNA miRNA Inhibitors and miRCURY LNA miRNA Power Inhibitors. Varying the numbers and positions of LNA nucleotides in these DNA/LNA mixmer inhibitors and carefully choosing the target sequences normalizes the melting temperatures of the oligonucleotides within a narrow window around an empirically determined optimal high temperature (see figure
Overall features of the third-generation miRNA inhibitor design). These design features ensure that miRCURY LNA miRNA Inhibitors have the same high efficacy, regardless of the GC content of their miRNA targets.
We provide the following two types of miRNA inhibitors:
- miRCURY LNA miRNA Inhibitors: these have normal phosphodiester nucleotide bonds, which are highly effective in most standard experiments
- miRCURY LNA miRNA Power Inhibitors: these have fully phosphorotioate (PS)-modified backbones, which are useful for challenging applications, such as difficult-to-transfect cell lines
miRNA silencing without transfection reagents
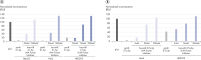
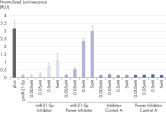
The combination of LNA and phosphorothioate modifications dramatically improves the stability of miRCURY LNA miRNA Power Inhibitors against enzymatic degradation, so the efficacy of Power Inhibitors is significantly better than the regular inhibitors (see figure
Enhanced potency of miRCURY LNA miRNA Power Inhibitors.
HeLa cells were transfected with a plasmid with a Renilla luciferase (transfection efficiency control) and an hsa-miR-21-5p target sequence in the 3'UTR of a Firefly luciferase reporter gene. Firefly luciferase expression is therefore suppressed by the corresponding endogenous miR-21-5p level in the cell. The next day, the cell cultures were transfected with different concentrations of regular and Power miRCURY LNA hsa-miR-21-5p inhibitors and negative controls. Reporter gene expression was measured with a dual Luciferase assay 24 H after transfection. Ratios of firefly and Renilla luciferase activity were calculated and normalized to values obtained with a firefly luciferase reporter with no miR target sequence (pLuc). The results illustrate that our miRNA inhibitors display sub-nanomolar potency under optimal transfection conditions, and the Power inhibitors display superior activity compared with the regular inhibitors.
 miRNA silencing via direct uptake (gymnosis) of Power Inhibitors.
miRNA silencing via direct uptake (gymnosis) of Power Inhibitors.